

Beyond the Pink Ribbon
(Navigating Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment)
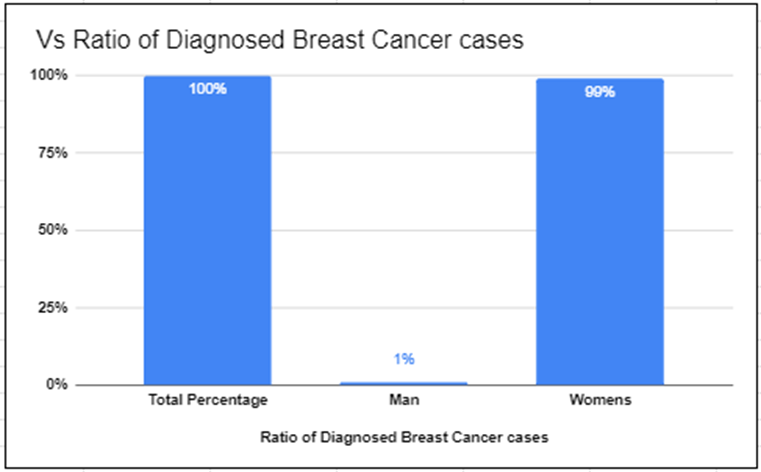
In recent years, breast cancer has displaced lung cancer as the most widespread kind of cancer in general, leading to an increase in the worldwide death rate in women. A multitude of risk factors, can provide to the growth of this cancer such as ageing, gene mutations, oestrogen, and so on but none of these variables can ensure that the incidence of breast cancer is accurately demonstrated. Breast cancer is always an unclear illness that develops quickly if a patient is not checked for it on an annual schedule. Breast cancer is complex and heterogeneous disease that remains a major complication to people, families, and healthcare systems around the world. The World Health Organisation (WHO) states that although breast cancer may affect men as well, it affects women much more frequently. The ratio of women to men diagnosed with breast cancer is approximately 100 to 1. This means that for every 100 cases of breast cancer diagnosed, approximately one case will be in a man but it is most ordinary in women. While breast cancer in men is rare, it's important to note that it does occur. Men account for less than 1% of all breast cancer cases, but the incidence has been gradually increasing over the years. The risk factors, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options for breast cancer in men are similar to those for women, although the disease may present differently due to differences in breast anatomy and hormonal profiles.In order to help people in their journey with breast cancer, there is an increasing need for thorough
education and knowledge due to developments in research and medical technology. This offers to provide an in-depth analysis of breast cancer, including a wide range of topics such as description, epidemiology, risk factors, preventing strategies, techniques for early detection, diagnostic processes, treatment alternatives, survivability, and available resources.
One kind of cancer that starts in the breast tissue cells is called breast cancer. It happens when abnormal breast cells grow or develop out of control, resulting in a tumor. These growths may either be benign indicating they are non-cancerous, or malignant indicating they are cancerous. Malignant tumors possess the capability to infiltrate nearby tissues and spread to other areas of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system, this phenomenon known as metastasis. Although it is significantly more common in women, the condition can affect men as well. Breast cancer can appear as a lump, thickness, or alteration in breast size or shape. It can also originate in the connective tissue, ducts, or lobules of the breast.
Characteristics of Tumors or Growth in the Breast Tissue: The characteristics of tumors or growths in breast tissue are important in understanding the nature and potential of breast condition that are given below.
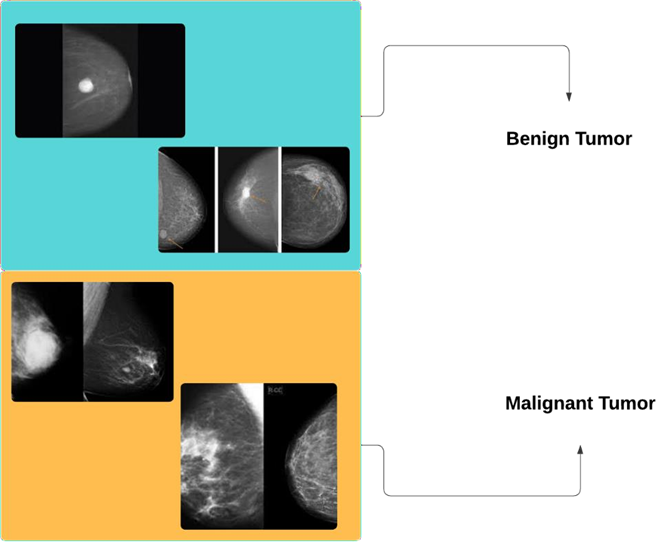
Categories - Breast Cancer: These categories of breast cancer, which can be categorized according to several of factors. Some main categories of breast cancer are:
Management Techniques - Breast Cancer Detection: A variety of medical techniques such as screening and early detection, diagnosis, treatment, and supportive care, are used to treat different forms of breast cancer. There are some techniques to handle breast cancer
Best Method for Diagnosis: Mammography, or biopsy is the most effective methods for detecting breast cancer. MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging) is considered to be the best method for determining an individual's high risk of developing breast cancer.
How Can Machine Learning Apply to Identify Breast Cancer?
Many machine learning techniques such as SVM, Decision Trees, and Neural Networks can be used to identify breast cancer. By using these algorithms, we are able to detect cancer at an early stage, which helps to slow down the disease's spread and improve the patient's chances of survival.
Dataset: We’ll be using the Mammography Mass Diagnostic dataset. This dataset allows the prediction of mammographic mass lesion severity (benign or malignant) based on BI-RADS characteristics and patient age. Let's examine the code now.
This objective of model to predict the type of breast cancer (benign or malignant) based on a number of features, such as the patient's age, the mass's shape, density, margin, and BI-RADS assessment. To perform the classification, the model makes use of a dense neural network architecture with binary cross-entropy loss function and rectified linear unit (ReLU) activation functions.
Project Pipeline: The steps in the project pipeline are as follows:
The relevant libraries for data analysis are imported like pandas for data manipulation, and numpy used for numerical operations, matplotlib for py.ploting, seaborn used for data visualization and scikit-learn for machine learning task. It focuses on using TensorFlow's Keras API to build and analyse neural network models.
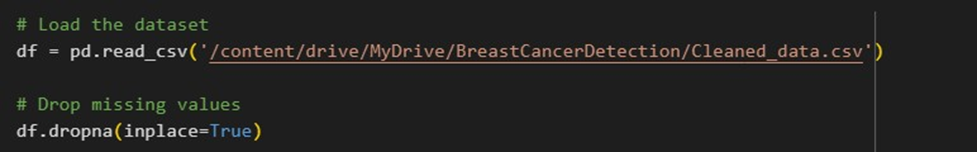
This method improves data cleanliness for additional analysis by reading a CSV file containing breast cancer data, loading it into a pandas DataFrame, and then removing any missing values from the dataset.
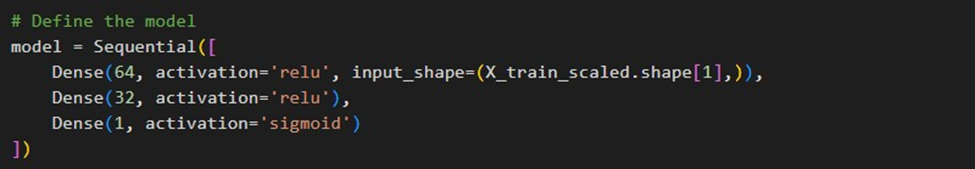
This ensures that the dataset is clean and prepared for analysis by filling in any missing data with the most common value identified in each column.
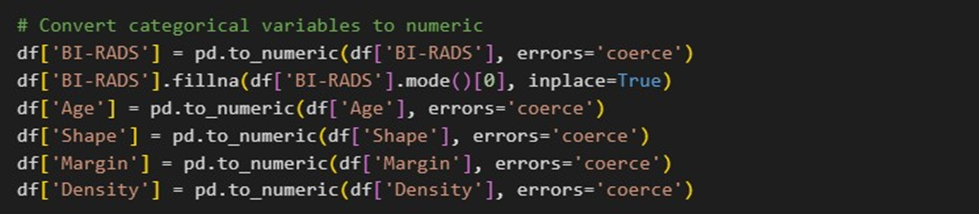
The dataset is divided into features (X) and the target variable (y) using this code segment. All columns in X are absent from the dataset; "Severity" is stored in y. It divides the data using an 80:20 ratio into training and testing sets.
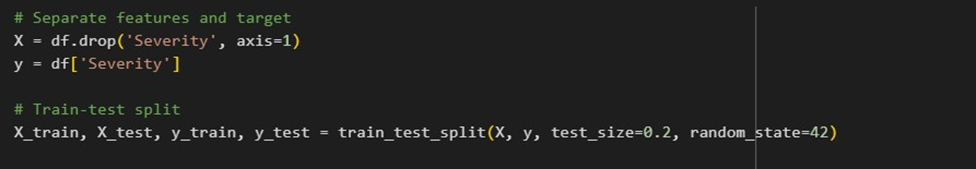
Adjusts the feature variables to have a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1 in order to standardise them. A StandardScaler object is first initialised, then applied using the fit_transform method to the training data (X_train) and the transform method.
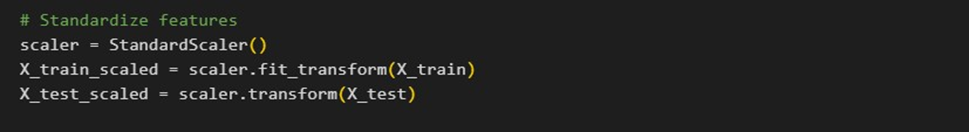
A feed forward neural network architecture known as a sequential model that uses ReLU activation functions to create two hidden layers of densely linked neurons. The output layer has a single neuron that has a sigmoid activation function, making it appropriate for binary classification tasks.
Feed forward neural network model with accuracy as the evaluation metric, binary cross-entropy loss function, and Adam optimizer.

The neural network model using a 10% subset of the training data for validation and 20 epochs on the training data with a batch size of 32.

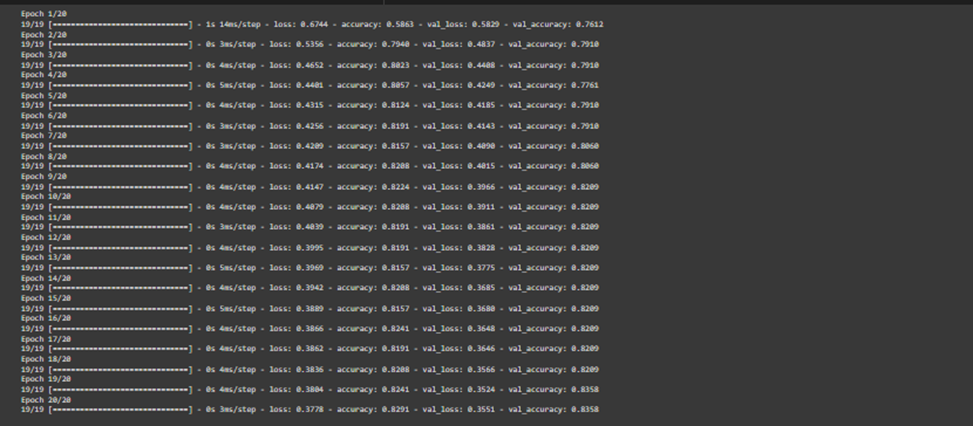
Step-9: Evaluation
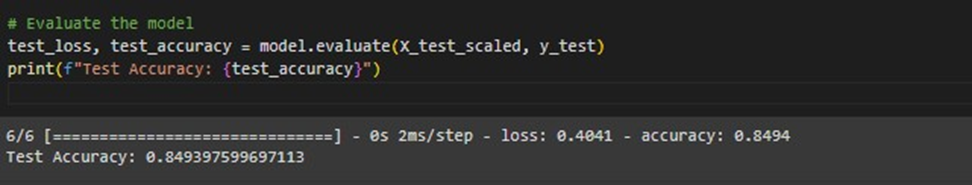
The trained model on the test data and prints out the test accuracy achieved by model.
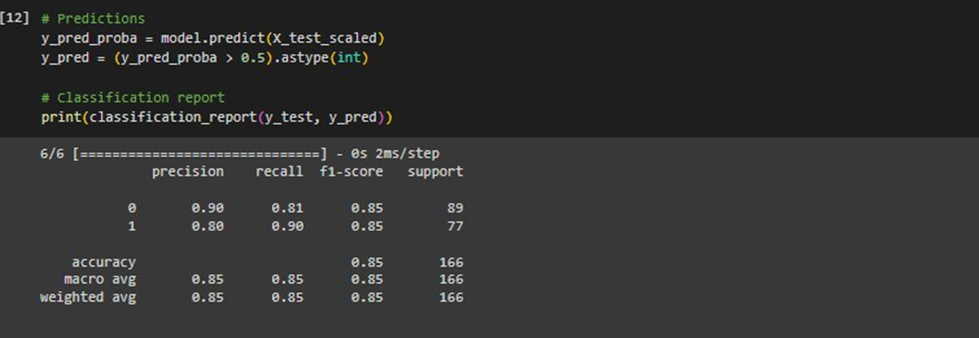
Using the trained model, this code makes predictions on the test data and provides a classification report with the precision, recall, F1-score, and support for each class.
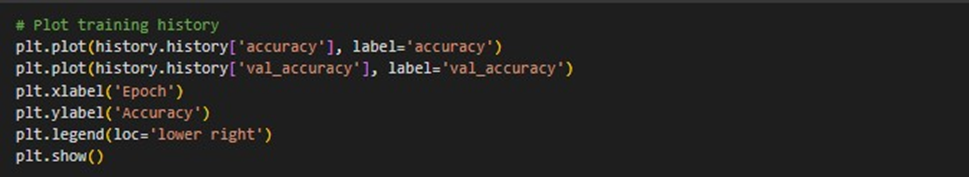
The accuracy of the model display on training and validation sets through epochs by plotting the model's training history. It provides visualizing the effects of overfitting and underfitting as well as changes in the model's performance throughout training.
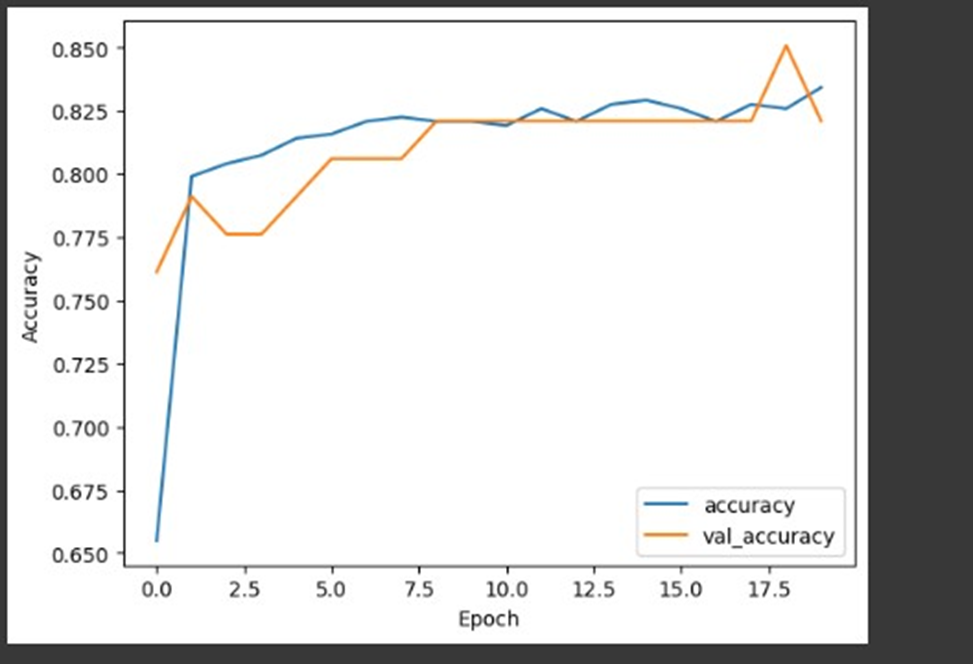
We could be able to prevent breast cancer in many cases and save many lives by improving the screening method's accuracy. By applying these machine learning and data visualization approaches, we can improve our awareness of the problems related to identifying anomalies in breast cancer data and make progress towards developing efficient treatment strategies.
Prevention and Risk Reduction:
In the end, "Beyond the Pink Ribbon" provides important information to patients dealing with breast cancer. Neural network developed to shows impressive accuracy in predicting the severity of breast cancer based on patient data. The training history shows how the model has learned over a number of epochs, showing its ability to recognie complex trends in the data and generate accurate predictions. This provides essential information in a simple to read manner, covers anything from identifying the disease and its risk factors to analysing screening methods, diagnosis procedures, and treatment possibilities. It also highlights the value of palliative care and survival programmes, as well as the need for further research and help to improve the quality of life for the breast cancer patient. Through the use of lifestyle modifications, genetic testing, and promoting for regular examinations, individuals can actively reduce their risk and keep their control over their journey towards breast cancer prevention.
Powered by Froala Editor