


Smart Companions: How AI and Robotics Are Easing Elderly Isolation
In the contemporary world, loneliness and social isolation among the elderly are complex and multifaceted challenges that significantly impact overall well-being. As people age, they experience substantial life changes such as retirement, bereavement, reduced mobility, and evolving social roles. These changes often lead to a decline in social connections and opportunities for interaction, resulting in heightened feelings of isolation. The consequences of this isolation are profound, including increased rates of anxiety, depression, and even suicide among the elderly.
Loneliness and social isolation among the elderly are pervasive issues with significant implications for mental and physical health. Several factors contribute to this problem:
Retirement often leads to the loss of social networks built around the workplace. Bereavement, especially the loss of a spouse, can significantly reduce social interactions. Reduced mobility and health issues can limit the ability to participate in social activities. These life changes create a perfect storm of conditions that can lead to profound feelings of loneliness and isolation. Social roles evolve, and the once-bustling social circles may shrink, leaving many elderly individuals to navigate their later years with fewer connections.

The psychological impact of loneliness is profound. Studies have shown that loneliness can lead to increased rates of anxiety, depression, and suicidal thoughts. The suicide rate among the elderly (aged 50 and above) is notably higher than among younger age groups. The World Health Organization reports that the suicide rate among the elderly is currently twice that of younger individuals. This alarming statistic underscores the critical need to address loneliness and isolation as public health priorities. Long-term loneliness can also lead to severe mental health issues, including anxiety and depression, potentially resulting in lethal nervous breakdowns.

Long-term loneliness is associated with various health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, weakened immune systems, and cognitive decline. The odds ratio for anxiety and depression among socially isolated individuals is significantly higher. A study observed that the Odds Ratio for Anxiety and Depression with Isolation was 1.14 (95% CI), highlighting the substantial mental health risks associated with social isolation. Additionally, loneliness can exacerbate physical health problems, leading to a cycle where poor health further reduces social interaction, deepening the sense of isolation.

The aging population is not evenly distributed globally. According to WHO, by 2050, 80% of older individuals will live in low- and middle-income countries. This rapid pace of population aging surpasses historical trends and poses unique challenges for these regions. In 2020, for instance, the population aged 60 and above surpassed the number of children under five, marking a significant demographic shift. The proportion of individuals aged 60 and above is projected to nearly double from 12% in 2015 to 22% by 2050.

To address these challenges, a comprehensive and multi-faceted approach is necessary. The WHO suggests several strategies, including:
Despite these efforts, traditional interventions may not be readily accessible to all older adults, especially those with limited mobility. This gap necessitates exploring alternative solutions leveraging current technology.
Socially Assistive Robots (SARs) present a promising solution to alleviate loneliness and provide care for older adults. SARs integrate advanced robotics and artificial intelligence to offer socialization and interactive relations, enhancing the well-being of users, particularly in healthcare and assisted living environments. These robots can be categorized into various types based on their functions:
Companion robots are designed to offer emotional support and companionship to individuals. They are equipped with features that enable them to engage in meaningful interactions with humans, providing comfort and reducing feelings of loneliness.

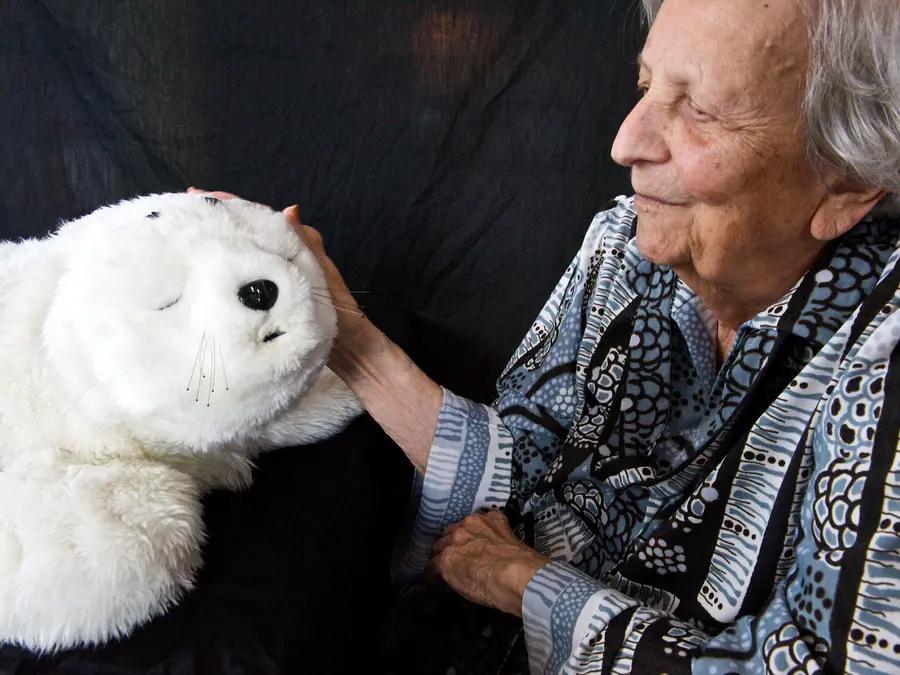
PARO, a therapeutic robot designed to resemble a baby seal, has been used in various healthcare settings to provide comfort and companionship to patients. Studies have shown that interacting with PARO can reduce stress and anxiety, improve mood, and increase social interaction among older adults. PARO has been particularly effective in dementia care, providing emotional support and cognitive stimulation.

Assistive robots are developed to help individuals with daily tasks that they may find challenging due to physical limitations. These tasks can include lifting individuals who have difficulty getting up, aiding in mobility and exercise, monitoring physical activity, detecting falls, assisting with feeding, and aiding in bathing or using the toilet. Assistive robots are essential in promoting independence and improving the quality of life for older adults.
Pepper, a humanoid robot developed by SoftBank Robotics, has been used in assisted living facilities to engage residents in social activities, provide information and reminders, and offer companionship. Pepper's ability to recognize and respond to human emotions has made it a valuable tool in enhancing the quality of life for older adults. Residents have reported feeling more connected and less lonely after interacting with Pepper.

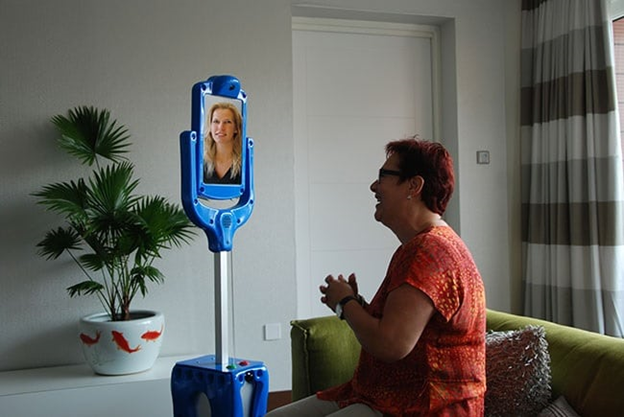
GiraffPlus is a telepresence robot designed to facilitate remote care for older adults. It allows healthcare professionals and family members to virtually visit and interact with the elderly, providing social interaction and monitoring health status. GiraffPlus has been used in pilot programs across Europe, demonstrating its potential to improve the well-being of older adults while enabling them to remain in their homes.

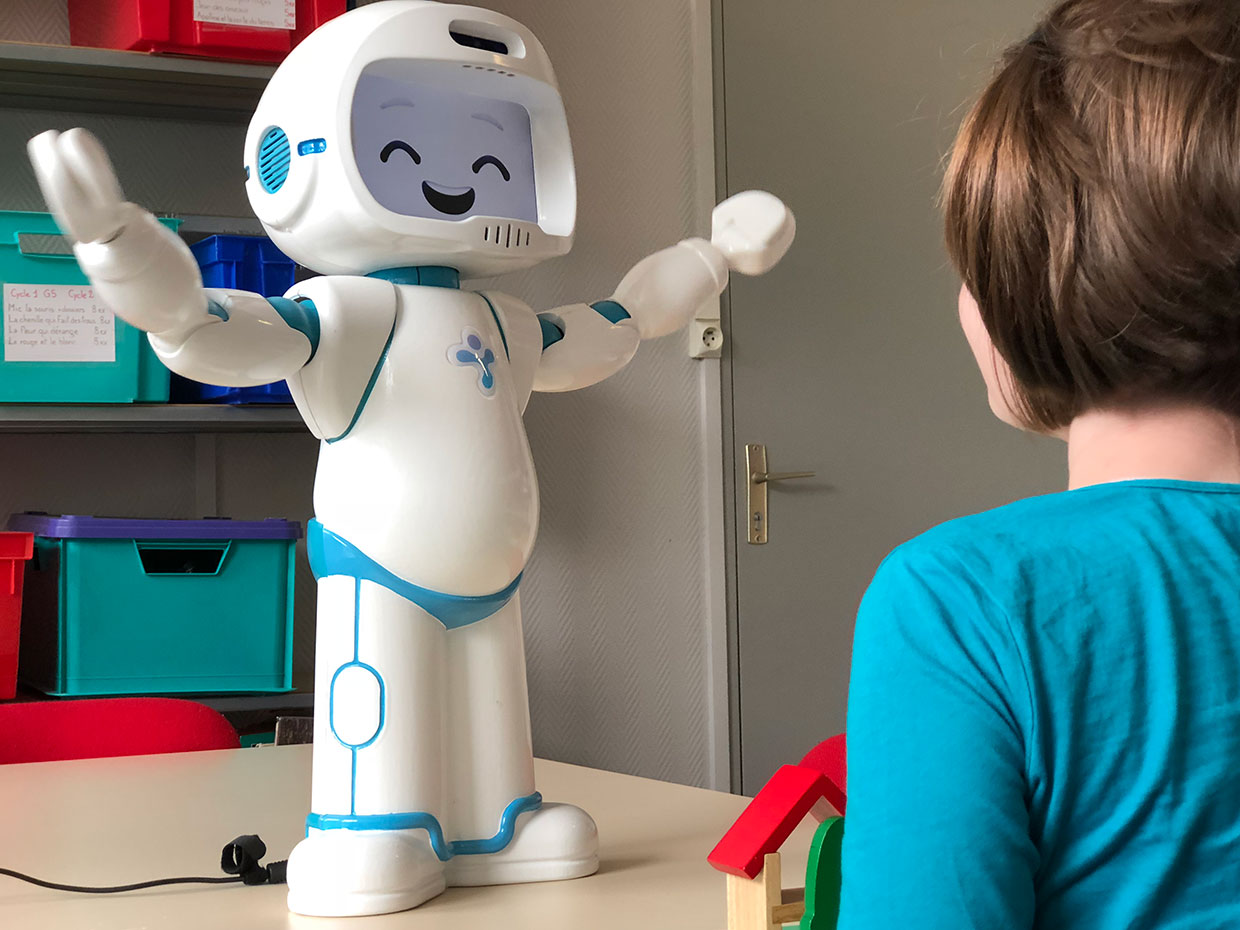
Therapeutic robots are designed to provide therapy and support for cognitive decline and mental health issues. They are used in healthcare settings to assist in the treatment of conditions such as dementia and Alzheimer's disease. These robots can engage in therapeutic activities, provide cognitive stimulation, and offer emotional support to patients, helping to manage and potentially reduce cognitive decline.

Robotic pets are designed to offer companionship and joy to individuals, particularly those who may not be able to care for a live pet. These robots can mimic the behavior of real pets, providing comfort and reducing feelings of loneliness. Robotic pets have been shown to have positive effects on mental health, reducing anxiety and depression in older adults.

The design of SARs follows a human-centered approach, considering the needs of all stakeholders and balancing human desirability, technical feasibility, and business viability. An important consideration is the Almere Model of Robot Acceptance, which incorporates factors such as sociability, social influence, perceived usability, and enjoyment relevant to the robot. This model helps ensure that SARs are designed to be user-friendly and effectively address the needs of older adults.
The Almere Model of Robot Acceptance is a framework that takes into account various factors that influence the acceptance and use of robots. These factors include:
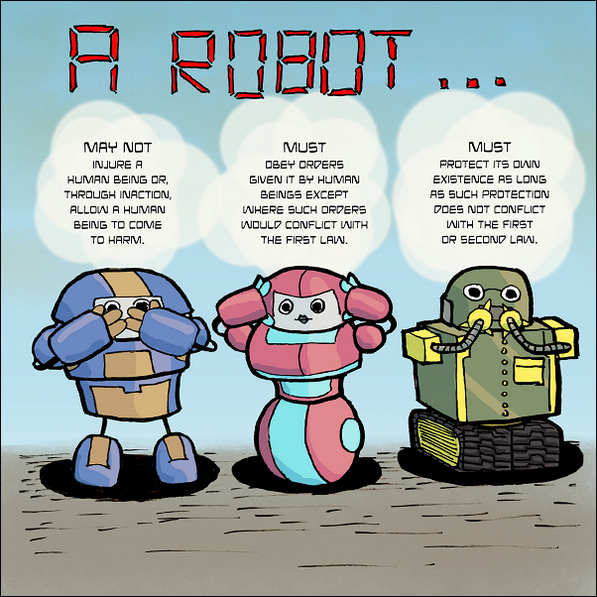
Care companion robots also adhere to the Three Laws of Robotics, ensuring the well-being and safety of both humans and the robots themselves:
Care companion robots are revolutionizing the landscape of healthcare and assisted living. They play a vital role in enhancing the well-being of individuals, particularly the elderly and those with disabilities. These robots offer personalized support and companionship, helping to improve the quality of life for their users.
Care companion robots can help healthcare professionals by performing tasks such as monitoring vital signs and reminding patients to take their medication. This support allows healthcare professionals to focus on more complex tasks, improving the overall efficiency of care.
In assisted living facilities or home environments, care companion robots act as constant companions, offering emotional support and engaging in conversations. They assist with daily activities, promoting independence and improving the quality of life for older adults.

The field of care robotics is rapidly growing, driven by the increasing need for caregiving support due to an aging population and advancements in AI and robotics. Technology experts predict a significant role for humanoids in healthcare in the future. Humanoids are expected to function as nurses and doctors, providing care for patients in hazardous situations and offering personalized support in various settings.
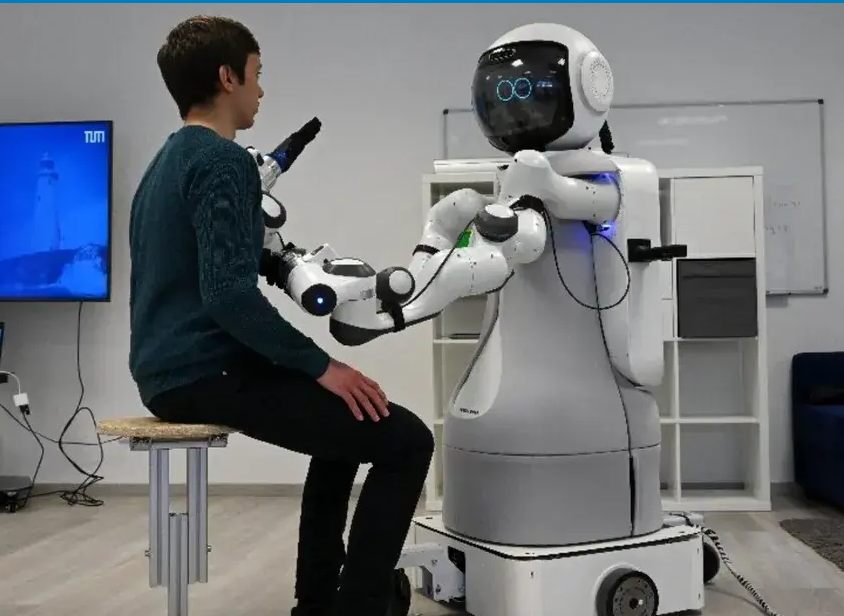

The integration of advanced robotics and AI in care companion robots represents a significant advancement in eldercare. By addressing the social, emotional, and health-related impacts of aging, these robots offer a promising solution to combat loneliness and improve the quality of life for older adults. Socially Assistive Robots provide personalized support, real-time health monitoring, and enhanced human-robot interaction in care settings, fulfilling multiple sustainable development goals.
As technology continues to evolve, the potential for SARs to revolutionize eldercare and healthcare is immense. The future of humanoids in healthcare is bright, with potential roles as nurses and doctors, providing care and support in various settings and enhancing overall efficiency in patient care. By embracing technological advancements, society can ensure that the aging population receives the care and companionship they deserve, paving the way for more personalized and effective support for individuals in need.
To fully harness the potential of SARs, it is crucial to continue research and development, addressing both technical and ethical challenges. Collaboration between technology developers, healthcare providers, and policymakers is essential to ensure that these robots are designed and deployed effectively and ethically.
Ongoing research and development are necessary to enhance the capabilities of SARs. This includes improving their ability to understand and respond to human emotions, increasing their autonomy, and ensuring their reliability and safety. Research should also focus on optimizing the robot's physical design, including mobility, durability, and ease of use.

Ethical considerations must be at the forefront of SAR development. This includes ensuring that the robots respect user privacy and autonomy, do not replace human caregivers but rather complement their efforts, and are accessible to all individuals, regardless of socioeconomic status. The development of SARs should adhere to ethical guidelines and principles, such as the Three Laws of Robotics, to ensure they are used for the benefit of society.
Policymakers play a critical role in the integration of SARs into healthcare and eldercare settings. Regulations should be established to ensure the safety and efficacy of these robots. Policies should also address issues related to data privacy and security, as SARs will likely collect and process sensitive health information.

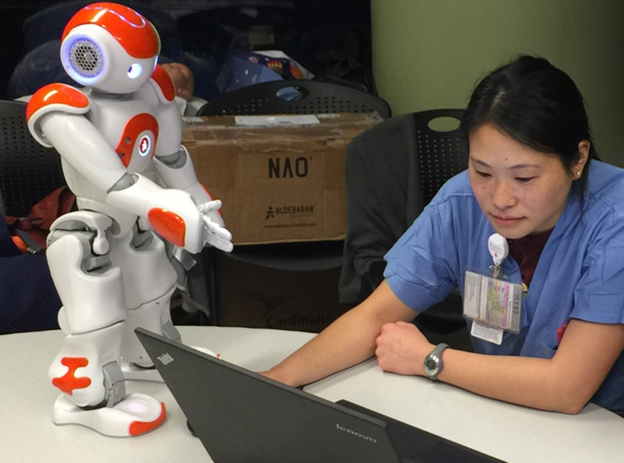
Education and training programs are essential to prepare healthcare professionals and caregivers to work alongside SARs. This includes training on how to operate and maintain the robots, as well as understanding their capabilities and limitations. Education programs should also be developed for older adults to help them feel comfortable and confident in interacting with SARs.

The future of Socially Assistive Robots in eldercare and healthcare is promising. These robots have the potential to transform the way care is provided, offering personalized support, enhancing emotional well-being, and improving overall quality of life for older adults. By embracing technological advancements and addressing ethical and practical challenges, society can ensure that SARs become valuable allies in the quest to combat loneliness and improve eldercare.
As we move forward, it is essential to continue investing in research and development, fostering collaboration among stakeholders, and ensuring that ethical considerations guide the design and deployment of SARs. By doing so, we can create a future where older adults receive the care and companionship they deserve, paving the way for a more inclusive and supportive society.
Powered by Froala Editor