


Brief Review of Virtual Reality
Virtual reality is defined as the actual, computer-generated environment that surrounds the user providing them with a real-life-like experience when they are wearing a headset that has 3D near-eye displays which are accompanied by position tracking. The result is accomplished by utilizing the VR headsets which feature display devices, sensors, and input means that help detect the movements and realign the virtual environment from the changes in physical motion. Furthermore, there are realistic and imaginary possibilities for the environments of VR, to offer a broad variety of experiences that range from real life or even invent new ones. The technology is built in such a way that it uses 3D graphics, sound, and interactivity mechanisms for users; therefore, it is a versatile tool for many applications: entertainment and for educational, health care, and training purposes.
Education as a sector has gone through a very drastic change over the past few decades with the advancement of technology at the forefront. Going from the use of personal computers and the internet in learning years back to the use of education technology systems and platforms now, the application of technology in education has brought about changes in how teachers teach and the methods through which students learn. Today’s technologies such as whiteboards, tablets, and numerous online tools have become almost mandatory tools in a contemporary classroom since they make learning a much more interactive, convenient, and fun experience. Adaptive learning is another way in which the use of technology in education is meant to meet the needs of different students, and learning styles and absolves inequalities in education. As new technologies such as AI, ML, and VR enter into the market opportunities to develop unique and much more interactive educational interfaces are introduced.

This blog seeks to explore what is the role of virtual reality in education. As an emerging technology, VR holds the promise of revolutionizing traditional educational methods by offering immersive, experiential learning opportunities that go beyond the capabilities of conventional teaching tools. By exploring various aspects of VR in education, including its benefits, challenges, and future prospects, this blog aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how VR can enhance learning outcomes and prepare students for a technologically advanced world. We will explore the possibilities of virtual reality (VR) to provide more inclusive, productive, and engaging learning environments through case studies, practical applications, and perspectives from educators and students.
Virtual Reality (VR) is defined as the technology that offers an environment that is almost real and can provide everyone with a feel of the real world albeit a fake environment. The VR headset gives the users a sensory experience that imagines them into a three-space dimension where they have to physically engage with objects in the place as if they were there. It aims to make the audience have an impression of such genres through stereoscopic display, motion tracking, and spatial audio. Some of the types of environments in VR can correspond to real-life environments or be quite different from them, and VR is effectively employed in the fields of entertainment, training, education, as well as therapy.
VR relies on a combination of hardware and software components to create its immersive experiences: VR relies on a combination of hardware and software components to create its immersive experiences:

The concept of VR has been around for decades, evolving significantly over time: The concept of VR has been around for decades, evolving significantly over time:
1. Early Concepts and Prototypes:
2. 2000s-2010s:
3. 2020s and Beyond:
Virtual Reality (VR) extends usual learning-teaching methods in the education setting to create value. Compared to other teaching aids, VR enables the students to dive into a particular concept and engage with it in a way that the idea seems more realistic. Due to those factors and characteristics that have been discussed above, information acquired through the use of VR could help reinforce and add value to conventional lectures, textbooks, and other classroom activities. That is why integrating these two types of activities is effective, as it adapts to the differences in learners’ abilities and provides them with different approaches to understanding the materials.
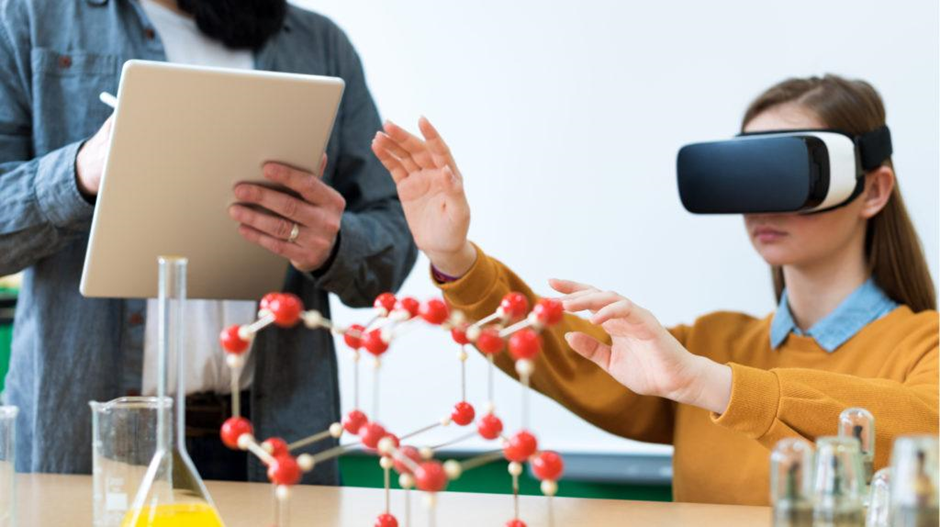

Immersive Learning Experiences
VR provides highly engaging forms of learning through which students can learn more about the topic of study than through the regular modes of learning. For example, instead of going through a chapter on ancient Rome, one can model walk down the Roman streets, see the landmarks, and feel like one is in Rome. This results in an increase in the level of interest simply because the time dedicated when learning is vacant of any other interruptions this enhances understanding of the content and makes it easier for learning to be retained.
Increased Engagement and Motivation
Another interesting finding of this study is the effect of VR on the engagement level or motivation of the students. The ability to effectively engage with students because of the highly participative component of VR is a strong suite of VR. Hence, one can support the opinion that increased engagement of students in the process of their learning retains their interest in classes much more effectively. Besides, challenges and rewards related to VR also improve motivation by making the learning process fun and a kind of game.
Improved Retention and Understanding
Some published research indicated that, compared to the traditional methods, VR enhances learners’ knowledge and retention of information. The tours possible with the application of VR make students embrace the third dimension to visualize and interact with data in a way that would make them understand it fully and, in the process, remember it. For instance, medical students use VR to learn about the human anatomy to explore the human body, how it works inside, and how the different systems of the body are interconnected unlike what is described in a learning manual. Thus, the practical approach of using models enhances understanding and enables the retention of knowledge for much longer.
Virtual Field Trips
Virtual reality makes it possible for students to undertake field trips virtually hence leaving the classroom. They can immerse themselves into artificial worlds and travel to actual places such as historical sites, museums, outer space, and so on, for places and events one cannot physically access. Virtual field trips also come with the added benefits of being cheaper and easier to manage as a usage of teaching techniques to enhance exposure that students get in class.

Simulations and Lab Experiments
In Safety Training many contexts, and scenarios that are either dangerous or too expensive to be recreated can be safely and accurately recreated in Virtual Reality. For example, chemistry learners can carry out practical lessons involving dangerous chemicals without posing any danger to their lives, or biology learners can get very close to microscope subjects. These simulation models offer practical knowledge without the usual consequences besides the costs because it sharpen the practical experiences. 
Historical Recreations
With the help of VR, it is possible to represent history and certain periods in such a way that would enable a student to study with personal presence. It can enable them to see certain occurrences, know the surrounding conditions and consequences, and also develop a better perception of the historical personalities and general milestones. Such representations enhance the history lessons’ quality and relevance and facilitate the learners’ grasping and retention of historical events and chronicles.

Interactive Storytelling
VR provides interactivity and personal involvement in the narration and the storyline. By using scenarios, students can be turned into characters in a story and make choices and their outcomes are felt in a simulation manner. This approach can be really useful for such subjects as literature, social studies, and ethics because children can develop critical thinking and empathy during the simulation.
When implemented in education, VR provides a means of enriching learning with the added means of augmenting the conventional paradigms of teachings, students’ interaction, and information comprehension. The examples of the application of virtual reality in pedagogy show that it has all the possibilities to become a driving force in terms of innovations in the sphere of learning and teaching, making the process more efficient and even fun.

Examples of Schools and Universities Using VR
Several schools and universities worldwide have successfully integrated VR into their educational programs, demonstrating its potential to enhance learning:
These case studies and success stories show how much VR has already influenced Education. Better students’ performance and the favorable attitude of teachers and students prove that VR has a high capacity to redefine and improve the learning process. In this case, the use of VR in educational institutions allows for the offering of new and meaningful learning experiences that will be useful in the future.
Cost of VR Equipment and Software
Another barrier to immersing it in learning is that VR hardware and software are costly. Note that the better and more advanced virtual reality headsets are costly, and may go for as high as several hundreds of dollars for each headset like the Oculus Rift or HTC Vive. Besides headsets, schools and universities require powerful computers to operate the VR applications, which can also drive the costs up. However, additional software such as educational applications and licensing and the additional software is also another financial addition. For many educational institutions especially the ones with limited budgets, these costs can be too expensive.
Accessibility and Digital Divide Issues
Adapting Curriculum to VR Content
Integration of VR into teaching and learning practices should be approached with cautionary measures though it is quite possible to infuse it into the curriculum. Some neoclassic instructional resources and techniques may not easily adapt well to virtual reality environments. Teachers should create, or look for, content for VR that fits the objectives of learning enriches the curriculum, and not only incorporates the technology as an extra installation. This takes time and possibly involving other experts in VR developers and educational technologists for the development of good and fruitful lessons using VR.
Training Teachers to Use VR Effectively
Potential for Motion Sickness
Vomiting or motion sickness is among the major side effects of using VR. When focusing on the disadvantages, it is necessary to note that the VR can sometimes provoke dizziness and nausea which are accompanied by discomfort and can often appear when the user experiences motion sickness when using VR or if the VR content includes high levels of motion. This may be a result of various things such as this affecting the concentration and attentiveness of the students. These effects suggest that abrupt movements should be avoided in the design of VR content to reduce the effects on the users’ bodies. Moreover, educators must ensure that students do not get uncomfortable with the use of VR by taking breaks occasionally.
Managing Screen Time
Following the adoption of most devices in learning, the issue of the time spent on screens is well observed. Excessive use of VR can also lead to increased screen time and its negative effects such as affecting the health of the students. Included among them are eye strain, headaches, and sleep disruption possibly due to disruption of the circadian rhythm. It leads to the call for moderation in the use of VR in teaching so that other forms of teaching are also incorporated to enable students to have a considerable amount of rest and or be engaged in physical activities. It is crucial to develop strict rules for VR usage to prevent negative outcomes for the students’ health.
That said, this paper has sought to address some of the challenges and considerations that educators and institutions have when seeking to incorporate VR into learning environments. Despite this, the potential of VR can be substantially high from the learning perspective, however planning, investing and support are significant to overcome these challenges and make VR a tool that can more effectively and safely provide the enhancement to learning.
Potential Advancements in VR Technology
Improved Hardware and Software
There is so much potential for VR to be used in future education as there are major improvements are expected to be seen in both the equipment and frameworks

Greater Accessibility and Affordability
As VR technology advances, it is expected to become more accessible and affordable:
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Enhancing VR Education
Artificial Intelligence (AI) will play a crucial role in advancing VR education:

Predictions and Trends for the Next Decade
The next decade is likely to see several key trends and developments in VR education:
Summing up the Possible Advantages and Disadvantages of Virtual Reality Use in Learning
Moreover, Virtual Reality (VR) has its advantages for the process of education which can change the view of learning offering different opportunities to present materials through immersive, engaging, and interactive technologies. The potential benefits include:
However, several challenges need to be addressed: However, several challenges need to be addressed:
A few concluding remarks on the essentials of VR in the education environment
The potential of VR in education is immense and using the abilities of VR there is expected to witness massive growth in the future due to the improvement of technology about the VR. It can be known that the VR hardware and software grow along with the environmental elements and with time the simulation in VR will become even more realistic. The integration of artificial intelligence will, in addition, boost the value of VR by creating courses that are unique and suitable for individuals based on the users’ preferences and specialties.
The presence of VR in the classroom is expected to change in the next decade resulting in a change of the landscape of learning with the implementation of augmented reality as a standard teaching tool as a means of teaching students in the physical world as well as the virtual world. Extended education and professional development shall also be enabled through VR which will enable people to be able to learn throughout their lifetime.
Incentives for Educators and Institutions to Plan for VR Futures
Many researchers and educators are urged to discover the possibilities existing in VR technology. Thus, with the help of VR, they can develop interesting, engaging, and highly effective learning experiences that will improve student comprehension and performance. However, the Social VR known in Education has its challenges that must be met; the possible advantages of Virtual Reality are numerous and may provoke revolutionary changes in the process of Education for the active and effective.
Purchasing programs, offering enrichment for educators, and offering equal access are some strategies for incorporating VR into learning. In becoming pioneers in this type of revolution in educational technology, educators and institutions as well can spearhead the way in molding students for a future where enhanced forms of learning are applied.
References
Powered by Froala Editor